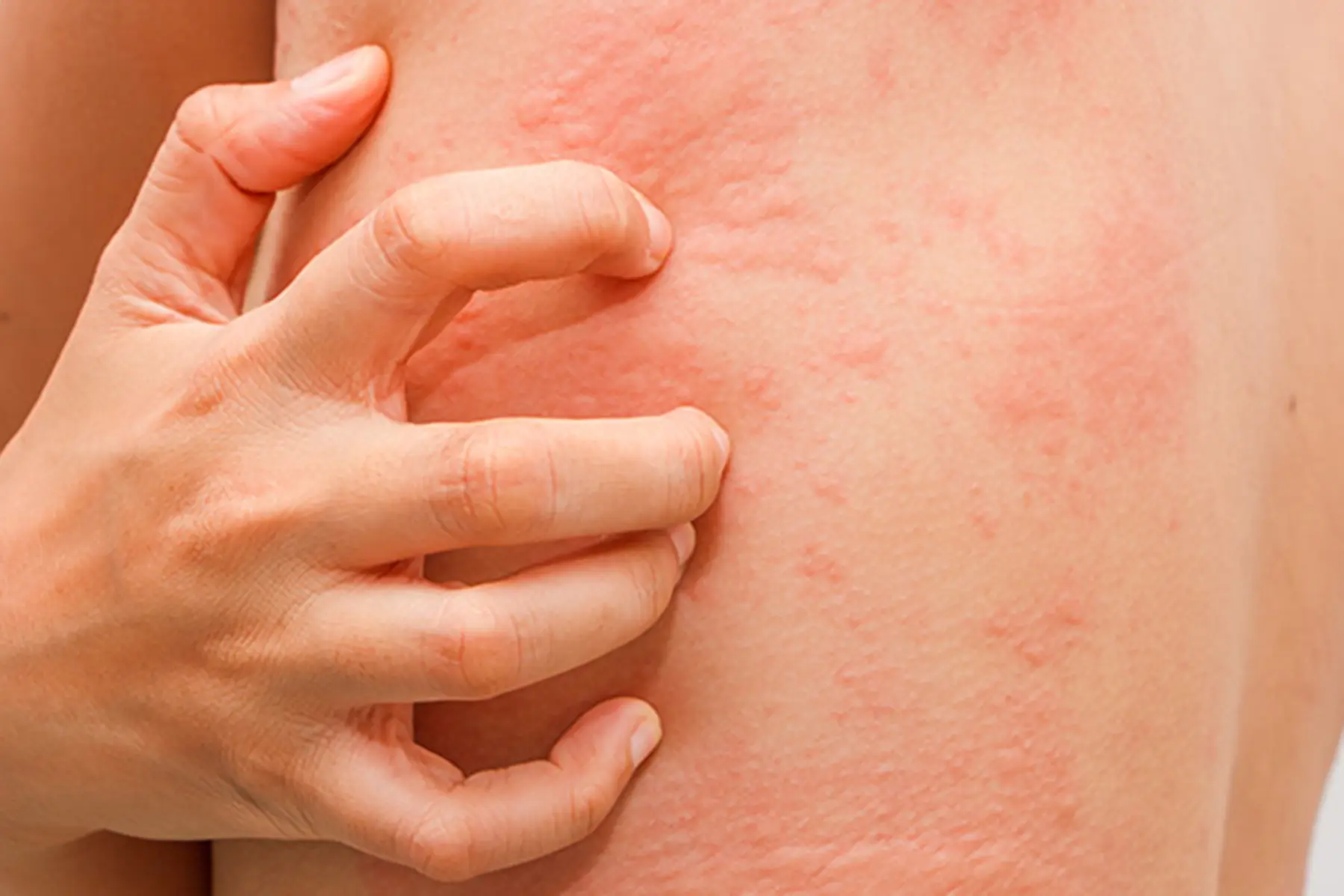
If you experience skin disorders such as acne, eczema, or hives, considering amoxicillin can be beneficial. This antibiotic often treats bacterial infections that may contribute to these conditions. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine if this medication is appropriate for your specific situation.
Amoxicillin works by targeting the bacteria responsible for infections. Its effectiveness can lead to noticeable improvements in symptoms, especially if the underlying cause of your skin disorder is bacterial. Common skin disorders that may respond well include inflammatory acne and certain types of dermatitis. Pairing amoxicillin with topical treatments often enhances your results.
Monitoring your body’s response to amoxicillin is key. While many patients report positive outcomes, some may experience side effects like rashes or allergic reactions. Communicate openly with your healthcare provider about your experience to adjust your treatment as needed.
In addition to antibiotic therapy, consider lifestyle changes to support skin health. Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and practicing good skincare routines can significantly impact your overall skin condition. Proper management of stress and regular exercise also contribute to skin’s appearance. Together with amoxicillin, these efforts can lead to healthier skin.
- Amoxicillin and Skin Disorders
- Identifying Allergic Reactions
- Management of Skin Reactions
- Understanding Amoxicillin and Its Uses
- Common Skin Disorders Treated with Amoxicillin
- Mechanism of Action of Amoxicillin on Skin Infections
- Bacterial Targets
- Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin on the Skin
- Allergic Reactions
- Other Skin Issues
- Identifying Allergic Reactions to Amoxicillin
- Guidelines for Amoxicillin Dosage in Skin Disorders
- Pediatric Dosage
- Duration of Treatment
- Precautions When Using Amoxicillin for Skin Issues
- Monitor for Allergic Reactions
- Consider Drug Interactions
- Interaction of Amoxicillin with Other Medications Affecting Skin
- When to Seek Medical Attention for Skin Reactions
Amoxicillin and Skin Disorders
Amoxicillin can lead to various skin reactions, such as rashes and allergic responses. If a rash appears after starting amoxicillin, discontinue use immediately and consult a healthcare professional. Some individuals may experience a maculopapular rash, which often presents as red spots and bumps on the skin. This reaction typically resolves once the antibiotic is stopped.
Identifying Allergic Reactions
Be alert for symptoms of a more severe allergic response, such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. These can indicate an anaphylactic reaction. If you notice these symptoms, seek emergency medical assistance right away. Keeping open communication with your doctor about any previous drug allergies is also beneficial.
Management of Skin Reactions
For mild rashes, antihistamines such as diphenhydramine may provide relief. Topical corticosteroids can also help reduce inflammation and itching. Always follow a healthcare provider’s guidance regarding the use of these treatments.
Documenting any skin reactions while on amoxicillin is crucial. This information can assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions for future treatments. Skin disorders related to amoxicillin often leave little long-term impact if addressed promptly.
Understanding Amoxicillin and Its Uses
Amoxicillin treats infections caused by bacteria, including skin disorders. It belongs to the penicillin class and works by disrupting bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to their destruction. This antibiotic effectively combats conditions like cellulitis, impetigo, and other skin infections.
Doctors often prescribe amoxicillin for specific infections, so following their guidance is crucial. Always complete the full course, even if symptoms improve. This prevents bacterial resistance and ensures that the infection is eradicated completely.
Keep an eye out for any skin reactions while using amoxicillin. Some may experience rashes or hypersensitivity. If these occur, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Monitoring your body’s response is important for safe treatment.
Regularly discussing your medical history and current medications with your doctor can help avoid potential interactions. Inform them if you have allergies, particularly to penicillin or cephalosporins.
Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet during treatment. This supports your immune system in fighting off infections effectively. Always prioritize communication with your healthcare provider for the best outcomes.
Common Skin Disorders Treated with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin effectively targets bacterial infections that affect the skin, making it a common choice for specific skin disorders. Conditions like acne vulgaris can benefit from its antibacterial properties, especially when secondary infections complicate the acne. Amoxicillin helps reduce inflammation and inhibits the growth of bacteria contributing to acne.
Cellulitis, characterized by painful, red swelling of the skin, often requires antibiotic treatment. Amoxicillin combats the bacteria responsible for this infection, leading to faster recovery and alleviation of symptoms. It is particularly effective in cases where the infection is mild to moderate.
Another condition, folliculitis, involves inflammation of hair follicles and can arise from bacterial infection. Amoxicillin helps manage this disorder by addressing the underlying bacteria, reducing redness and discomfort within a short period.
Impetigo, a contagious skin infection more common in children, responds well to amoxicillin. It clears up crusty sores caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal bacteria, promoting healing and preventing further spread among individuals.
For those suffering from skin abscesses, amoxicillin can facilitate recovery by treating the bacterial infection within the abscess. Proper drainage, coupled with antibiotic treatment, often results in a swift resolution.
While amoxicillin is effective against these conditions, consulting a healthcare provider remains essential for proper diagnosis and treatment tailored to individual needs.
Mechanism of Action of Amoxicillin on Skin Infections
Amoxicillin targets bacterial cell wall synthesis, blocking the transpeptidation enzymes that facilitate cross-linking in peptidoglycan layers. This disruption weakens the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell lysis and death, particularly in Gram-positive organisms commonly associated with skin infections.
Bacterial Targets
Amoxicillin is particularly effective against bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, both frequent culprits in skin disorders. By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), amoxicillin prevents these bacteria from forming a stable cell wall, rendering them unable to survive under osmotic pressure.
After oral administration, amoxicillin achieves peak plasma concentrations within 1-2 hours, ensuring rapid action against invading pathogens. It has good tissue penetration, allowing adequate concentrations to reach skin and soft tissues, which is essential for treating localized infections.
| Bacterial Type | Common Skin Infections | Amoxicillin Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive | Impetigo | High |
| Gram-positive | Folliculitis | High |
| Gram-positive | Cellulitis | Moderate |
| Gram-negative | Abscesses | Low |
Using amoxicillin for skin infections provides a reliable option, particularly against Gram-positive pathogens. Monitoring for resistance patterns is recommended to ensure its ongoing effectiveness in treatment protocols.
Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin on the Skin
Amoxicillin can lead to various skin reactions that require attention. Among the most common are rashes, which may appear as red, itchy bumps. These rashes can manifest within a few days after starting the medication. If a rash develops, monitoring its progression is essential. In some cases, these rashes may enhance in severity, warranting immediate medical consultation.
Allergic Reactions
An allergic reaction to amoxicillin may present with hives, swelling, or severe itching. These symptoms often require urgent care. Discontinuing the medication upon experiencing any signs of an allergic response is crucial. Individuals with a known allergy to penicillin should avoid amoxicillin altogether, as cross-reactivity can occur.
Other Skin Issues
Less common side effects include photosensitivity, causing increased burn risk after sun exposure. Users should take precautions, such as using sunscreen or covering exposed skin. Additionally, some patients might experience localized skin infections or changes in pigmentation, which can be distressing. Consulting a healthcare provider for any concerning symptoms is advised to explore alternative treatments and ensure skin safety.
Identifying Allergic Reactions to Amoxicillin
Monitor the skin closely for signs of an allergic reaction after taking amoxicillin. Immediate symptoms may appear within an hour or take several days to develop.
- Rash: A sudden appearance of hives or a red, itchy rash often indicates an allergy. Observe if the rash spreads or worsens.
- Swelling: Pay attention to any swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. This can signal a more severe reaction.
- Difficulty Breathing: Any trouble breathing or wheezing warrants immediate medical attention. Do not ignore this symptom.
- Itching: General itching without a visible rash can also suggest an allergic response. Keep track of its persistence.
If experiencing any of these symptoms, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional promptly. They may recommend alternatives or testing to confirm the allergy.
Keep a detailed record of symptoms to discuss with your doctor. This helps in determining the precise nature of the allergic reaction and ensures safe future treatment options.
- Note the time of occurrence.
- Document any previous reactions to antibiotics or similar medications.
- Share family history of allergies, as this may aid in diagnosis.
Always follow prescribed guidelines and reach out to a healthcare provider for additional concerns. Tracking your reactions and communicating effectively can ensure safer medication experiences in the future.
Guidelines for Amoxicillin Dosage in Skin Disorders
For the treatment of skin disorders caused by bacterial infections, the typical dosage of Amoxicillin for adults is 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours. Adjustments may be necessary based on the severity of the condition or patient response.
Pediatric Dosage
- Children weighing less than 40 kg: Administer 20 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses.
- Children weighing more than 40 kg: Use adult dosing guidelines (500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours).
Duration of Treatment
The duration typically ranges from 5 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection and clinical response. Regular reassessment is key to determining if continued treatment is necessary.
- Early improvement may suggest a shorter treatment duration.
- Persistent symptoms warrant reevaluation and possible culture tests.
Always consider individual patient factors such as renal function and history of allergy to penicillin when prescribing Amoxicillin. Consult a healthcare professional if needed to tailor the dose appropriately.
Precautions When Using Amoxicillin for Skin Issues
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting amoxicillin, especially if you have allergies to penicillin or other antibiotics. This ensures your safety and reduces the risk of adverse reactions.
Monitor for Allergic Reactions
Monitor your body after the first dose. Common allergic symptoms include:
- Rash
- Itching
- Swelling
- Difficulties in breathing
If any of these symptoms appear, seek medical attention immediately.
Consider Drug Interactions
Inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking. Certain medications may interact with amoxicillin and lead to reduced effectiveness or increased side effects. Pay particular attention to:
- Blood thinners
- Medications for gout
- Other antibiotics
Stay well-hydrated during treatment, as it can help your body process the medication effectively. Finally, avoid alcohol to prevent potential side effects and ensure the best outcome from your treatment.
Interaction of Amoxicillin with Other Medications Affecting Skin
Amoxicillin may interact with various medications that impact skin health. Combining it with other antibiotics, such as doxycycline, can reduce the effectiveness of the latter. Monitor for any signs of decreased efficacy when using these concurrently.
When using amoxicillin alongside retinoids, like isotretinoin, caution is advised. Both can cause dryness and irritation. Adjust dosages as needed to minimize these effects. Hydration and topical moisturizers may help alleviate skin discomfort.
Antihistamines, commonly prescribed for allergic reactions, can be used with amoxicillin; however, some sedating antihistamines may exacerbate skin dryness. Opt for non-sedating options if skin irritation is a concern.
Topical corticosteroids can effectively reduce inflammation while taking amoxicillin. Ensure appropriate dosing to prevent skin thinning, especially during long-term use. Regular monitoring is advisable.
When considering drug interactions, always consult with a healthcare provider. Tailoring medication regimens can greatly enhance skin health outcomes while managing underlying infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Skin Reactions
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience severe itching, swelling, or blistering after taking amoxicillin. These symptoms may indicate an allergic reaction that requires immediate care.
If you notice a rash that rapidly spreads or is accompanied by fever, seek help promptly. These signs could signal a more serious condition, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, which demands urgent evaluation.
Persistent skin reactions lasting more than a few days should also prompt a visit to your doctor. Delaying treatment can lead to complications or prolonged discomfort.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe itching | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Swelling or blistering | Consult a healthcare professional |
| Rapidly spreading rash | Visit an emergency room |
| Fever with skin reactions | Get evaluated at a medical facility |
| Persistent rash over multiple days | Schedule an appointment with your doctor |
Do not hesitate to reach out for help if you have concerns about your skin condition. Early intervention can prevent further complications and promote recovery.