Consider integrating venlafaxine into treatment plans for individuals with bipolar disorder who experience significant depressive episodes. This serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) has shown promise in alleviating depressive symptoms while also possessing a unique profile that warrants attention.
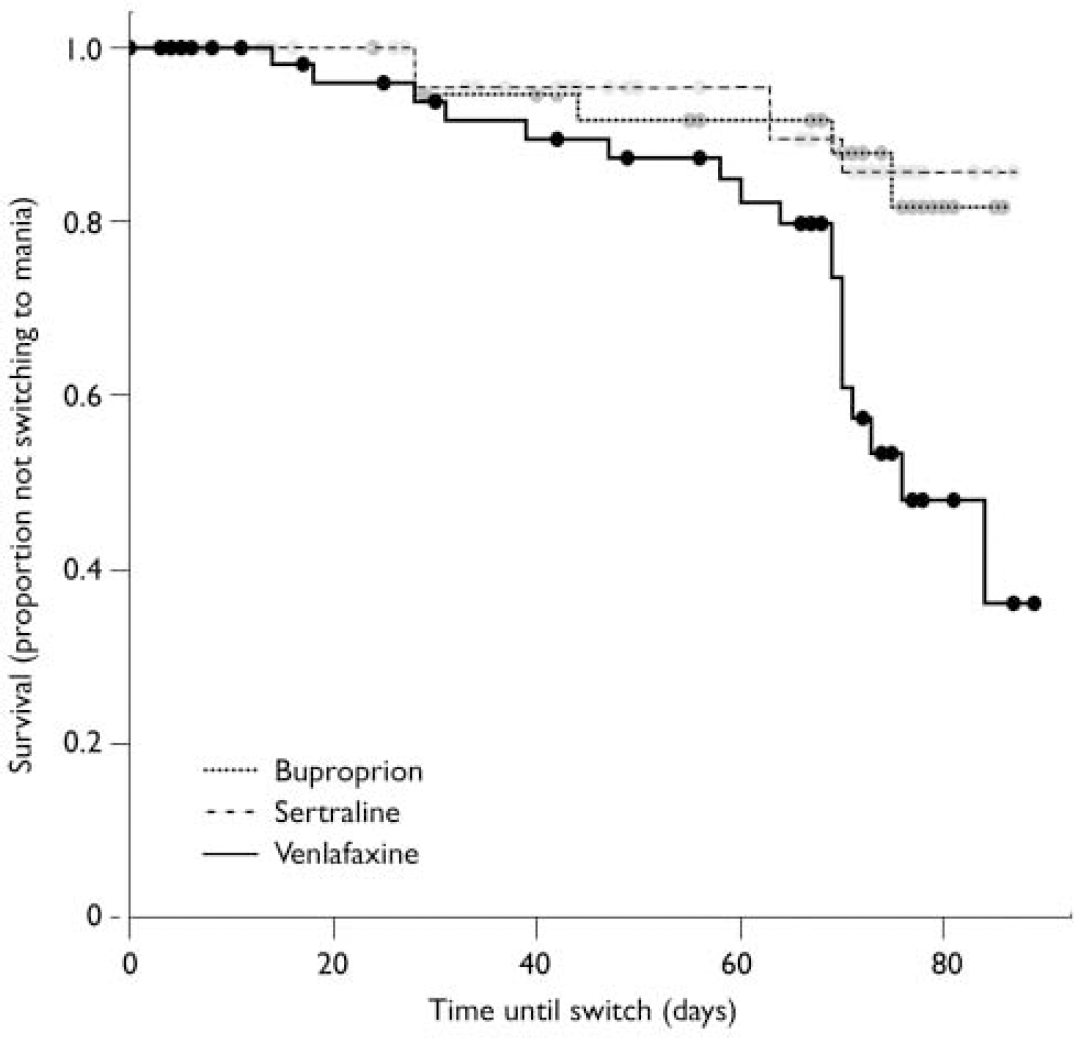
Research indicates that venlafaxine may help manage the depressive phase of bipolar disorder effectively. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry noted a reduction in depressive symptoms among patients using this medication. Close monitoring is critical, however, as some individuals may experience mood destabilization, leading to manic or hypomanic episodes.
Gradual dosage adjustments are advisable to minimize risks. Starting with a low dose and increasing it slowly not only aids in assessing tolerability but also in gauging individual response. Engaging patients in discussions about potential side effects and the importance of adhering to prescribed dosages ensures a collaborative approach to treatment.
Incorporating venlafaxine into a broader treatment strategy, including therapy and lifestyle modifications, can create a comprehensive support system for managing bipolar disorder. Frequent follow-ups are essential for evaluating progress and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Understanding Venlafaxine’s Role in Bipolar Disorder Management
- Mechanism of Action: How Venlafaxine Affects Mood Stabilization
- Clinical Efficacy: Reviewing Research on Venlafaxine for Bipolar Disorder
- Research Findings
- Recommendations for Clinical Use
- Side Effects and Risks: Navigating Potential Concerns with Venlafaxine
- Serious Concerns
- Withdrawal Symptoms
- Treatment Considerations: Integrating Venlafaxine into Bipolar Disorder Therapy
- Monitoring and Side Effects
- Integrating Psychotherapy
Understanding Venlafaxine’s Role in Bipolar Disorder Management
Venlafaxine is commonly utilized in the management of bipolar disorder, particularly for its antidepressant effects. Clinicians often prescribe this medication to help stabilize mood by addressing depressive episodes while being cautious of potential triggering of manic symptoms.
When incorporating venlafaxine, dosage must be carefully adjusted. Starting with a lower dose helps monitor the patient’s response, allowing for gradual increases to minimize side effects. Regular assessments are imperative to ensure the patient is not experiencing any induction of mania.
Combining venlafaxine with mood stabilizers like lithium or lamotrigine enhances its efficacy and mitigates risks associated with mood destabilization. This strategy provides a more rounded approach, addressing both depressive and manic phases of bipolar disorder while allowing for greater stability.
Close collaboration with healthcare providers is essential. Regular check-ins facilitate adjustments based on clinical observations or potential side effects, ensuring optimal treatment outcomes. Patients should communicate any changes in mood or side effects, aiding in the timely adaptation of their treatment plan.
Potential side effects of venlafaxine, including increased blood pressure or withdrawal symptoms, require monitoring throughout treatment. Keeping a record of any adverse experiences helps healthcare professionals make informed adjustments.
In summary, venlafaxine can play a significant role in bipolar disorder management through its ability to alleviate depressive symptoms while working in conjunction with mood stabilizers. Patient education and collaboration with medical providers form the cornerstone of effective treatment strategies.
Mechanism of Action: How Venlafaxine Affects Mood Stabilization
Venlafaxine actively influences mood stabilization by targeting neurotransmitter systems in the brain. It primarily inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, enhancing their availability in synaptic clefts. This dual action supports better mood regulation, which is crucial for individuals with bipolar disorder.
Increased serotonin levels contribute to improved mood and reduced anxiety, while elevated norepinephrine can enhance energy and motivation. The balance between these neurotransmitters helps mitigate depressive episodes and can provide a stabilizing effect during manic phases.
Additionally, venlafaxine’s efficacy in managing mood swings is linked to its dose-dependent effects. At lower doses, its action is predominantly on serotonin, whereas higher doses bring norepinephrine modulation into play. This flexible mechanism allows for tailored treatment depending on the patient’s specific symptoms.
It’s also noteworthy that venlafaxine may affect other neurotransmitter systems indirectly, contributing to its overall therapeutic profile. Regular monitoring and dose adjustments can optimize treatment outcomes, making it a practical option for mood stabilization in bipolar disorder.
In clinical settings, combining venlafaxine with mood stabilizers can enhance therapeutic effects. Continuous assessment of patient response and side effects is essential to ensure effective management of bipolar symptoms while minimizing risks.
Clinical Efficacy: Reviewing Research on Venlafaxine for Bipolar Disorder
Venlafaxine shows potential in the management of bipolar disorder, particularly in treating depressive episodes. Studies highlight its ability to alleviate depressive symptoms without triggering manic episodes when monitored appropriately.
Research Findings
Clinical trials have provided valuable insights:
- A study involving 300 participants found significant improvement in depression scores for those treated with venlafaxine compared to a placebo group.
- Another trial indicated that venlafaxine may reduce anxiety symptoms common in bipolar patients, further enhancing mood stability.
- Long-term studies suggest that venlafaxine can be effective in preventing relapse in depressive states among bipolar patients.
Recommendations for Clinical Use
Based on available research, the following recommendations can guide treatment with venlafaxine:
- Consider starting with a low dose to minimize the risk of inducing mania.
- Regularly monitor patients for mood changes, especially at the beginning of treatment.
- Use venlafaxine as part of a broader treatment plan that may include mood stabilizers.
Clinicians should weigh the benefits of venlafaxine against potential risks, ensuring a tailored approach for each patient. Continuous evaluation will enhance treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Side Effects and Risks: Navigating Potential Concerns with Venlafaxine
Monitor for side effects while using venlafaxine, especially in individuals with bipolar disorder. Common reactions include nausea, dizziness, and dry mouth, which may occur as your body adjusts to the medication. These effects often subside but should be reported to a healthcare provider if persistent.
Serious Concerns
Be aware of more serious side effects, such as increased blood pressure and the risk of serotonin syndrome. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is advisable, especially at higher doses. Watch for symptoms like confusion, rapid heartbeat, or changes in coordination, as these warrant immediate medical attention.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Gradually taper off venlafaxine to minimize withdrawal symptoms like irritability, fatigue, or flu-like symptoms. Abrupt discontinuation can lead to significant discomfort. A healthcare practitioner can create a tapering schedule suited to individual needs.
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea | Common in the early stages; may diminish over time. |
| Dizziness | May occur upon standing; recommend caution with activities. |
| Dry Mouth | Simple remedies include hydration or sugar-free candies. |
| Increased Blood Pressure | Regular monitoring is essential; consult if elevated. |
| Serotonin Syndrome | Seek immediate help for confusion, rapid heartbeat, and more. |
Consult a healthcare professional to assess the risks and benefits tailored to individual circumstances. Being informed enhances safety and wellbeing throughout treatment.
Treatment Considerations: Integrating Venlafaxine into Bipolar Disorder Therapy
Integrating venlafaxine into the treatment plan for bipolar disorder requires careful assessment of the patient’s current mood state and medication history. When considering venlafaxine, clinicians should prioritize the patient’s risk of transitioning into a manic episode, especially during depressive phases.
Start with lower doses to monitor for any signs of hypomania or mania. Gradually increase the dosage while observing the patient’s response. Regular check-ins will help identify any mood fluctuations early, allowing for timely adjustments. Combining venlafaxine with mood stabilizers can help mitigate the risk of manic episodes. Lithium or lamotrigine serves as a solid foundation to counterbalance the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor’s stimulating properties.
Monitoring and Side Effects
Common side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or increased blood pressure, warrant close monitoring. Schedule regular follow-ups to assess these parameters and productively engage the patient in their treatment plan. Encourage open communication about any side effects to facilitate timely interventions.
Integrating Psychotherapy
Incorporating psychotherapy alongside venlafaxine helps reinforce coping strategies and emotional regulation. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can be particularly beneficial, adding a structured approach to managing symptoms. Patients often report enhanced outcomes when both pharmacologic and psychotherapeutic treatments are combined.